-
2023 year in review
The research coming out of the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR) in 2023 ranged from fascinating to impactful. From La Niñas and El Niños to supercomputers named after wind and the impacts of literal wind, here are the highlights of NSF NCAR’s top science stories from the past year.
- Sun + Space Weather,
- Supercomputing,
- Water,
- Weather
-
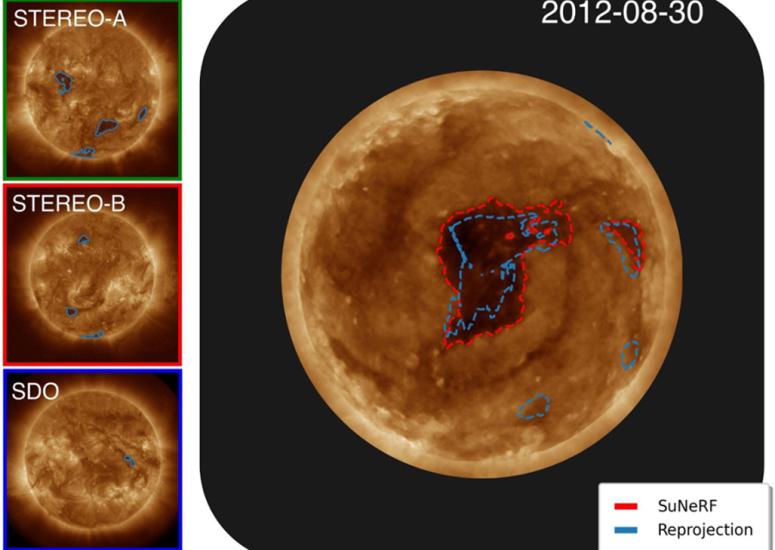
Virtual observatory provides first “look” at the solar poles
Scientists are turning to artificial intelligence (AI) to view the Sun’s poles — or at least produce an educated guess of what the Sun’s poles might look like, since they’ve never been observed before.
- Sun + Space Weather
-
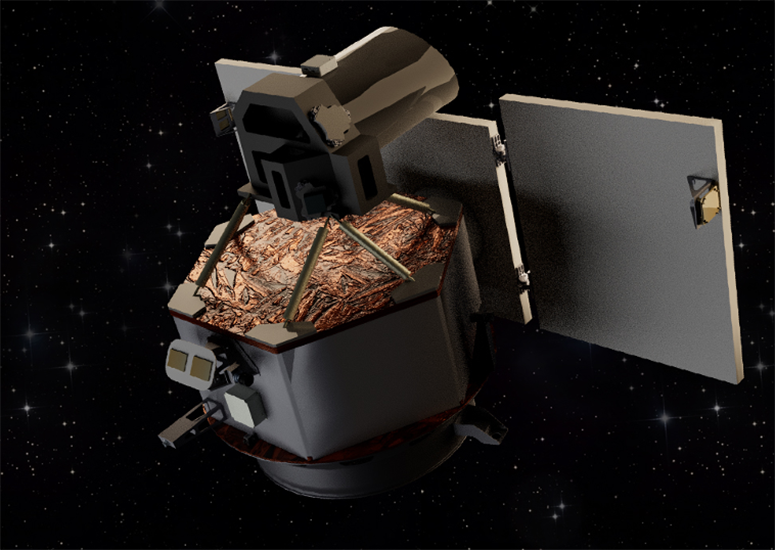
Shining light on a solar blindspot
A proposal for a spacecraft that would take a fresh look at the Sun — enabling a never-before-seen view of our star’s magnetic field — has received $2 million in funding from NASA for further study.
- Sun + Space Weather
-
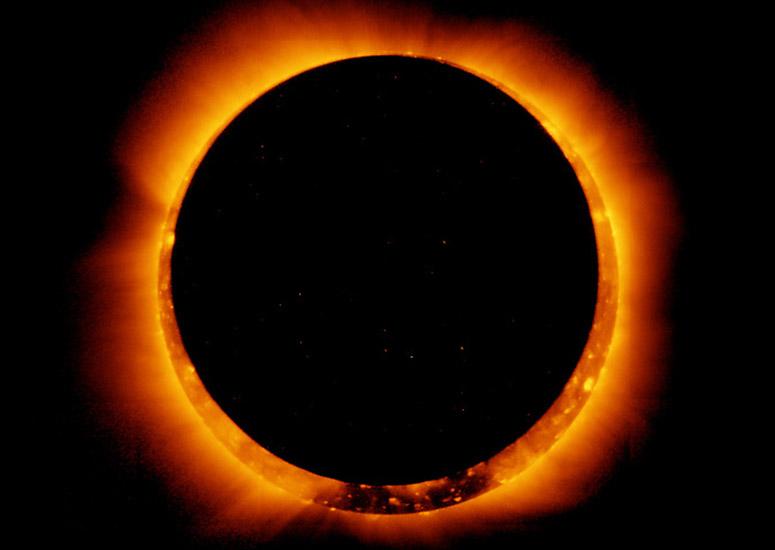

Join NCAR solar scientists in Utah to watch the Oct. 14 annular eclipse
Scientists from the High Altitude Observatory will be onsite at Hovenweep National Monument
- Sun + Space Weather
-
NASA funds NCAR solar mission
An NCAR-led project, CMEx, will attempt to understand the magnetic nature of solar eruptions and identify the magnetic sources of the solar wind.
- Sun + Space Weather
