Hurricanes and climate change: NCAR launches intensive study into future hurricane risk
Oct 8, 2008 - by Staff
Oct 8, 2008 - by Staff
BOULDER—The National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), working with federal agencies and universities as well as the insurance and energy industries, has launched an intensive study to examine how global warming will influence hurricanes in the next few decades. The goal of the project is to better inform coastal communities, offshore drilling operations, and other interests that could be affected by changes in hurricanes.
The project will use a combination of global climate and regional weather models, run on one of the world's most powerful supercomputers, to look at future hurricane activity in unprecedented detail. Researchers are targeting the hurricane-prone Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea to assess the likely changes, between now and the middle of the century, in the frequency, intensity, and paths of these powerful storms. Initial results are expected early next year.
"It is clear from the impacts of recent hurricane activity that we urgently need to learn more about how hurricane intensity and behavior may respond to a warming climate," says NCAR scientist Greg Holland, who is leading the project. "The increasingly dense development along our coastlines and our dependence on oil from the Gulf of Mexico leave our society dangerously vulnerable to hurricanes."
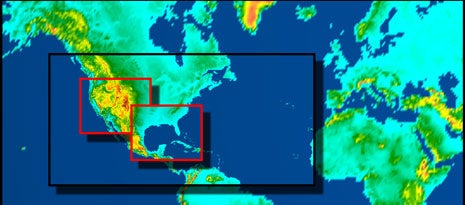 Zooming in on future climate. NCAR scientists are using a combination of weather and climate computer models to simulate the atmosphere in three dimensions at resolutions ranging from about 20 miles across a large part of the Northern Hemisphere to as fine as 2.5 miles in targeted areas of North America (red boxes). This strategy enables scientists to forecast future climate in detail for specific regions without overloading existing supercomputing resources.(Contrast between coarse and fine resolution has been increased for illustrative purposes; [ENLARGE] for best contrast. ©UCAR, image by Steve Deyo.) News media terms of use*
Zooming in on future climate. NCAR scientists are using a combination of weather and climate computer models to simulate the atmosphere in three dimensions at resolutions ranging from about 20 miles across a large part of the Northern Hemisphere to as fine as 2.5 miles in targeted areas of North America (red boxes). This strategy enables scientists to forecast future climate in detail for specific regions without overloading existing supercomputing resources.(Contrast between coarse and fine resolution has been increased for illustrative purposes; [ENLARGE] for best contrast. ©UCAR, image by Steve Deyo.) News media terms of use*
The new study follows two major reports, by the U.S. Climate Change Science Program (CCSP) and Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), that found evidence for a link between global warming and hurricane activity. But many questions remain about future hurricanes. For example, the CCSP report concluded that future changes in frequency were uncertain and that rainfall and intensity were likely to increase, but with unknown consequences.
Improved understanding of climate change and hurricanes is an especially high priority for the energy industry, which has a concentration of drilling platforms, refineries, pipelines, and other infrastructure in a region that is vulnerable to severe weather. Hurricanes Gustav and Ike damaged offshore oil production and several refineries, disrupting gasoline supplies.
The project is part of a larger effort examining regional climate change between 1995 and 2055. The simulations are being run on NCAR's bluefire supercomputer with support from the National Science Foundation, NCAR's sponsor, and through a long-term collaboration with the insurance industry through the Willis Research Network. Additional backing is expected from the Research Partnership to Secure Energy for America, a nonprofit consortium that includes the U.S. Department of Energy and several energy companies. The Georgia Institute of Technology is collaborating on the research, and other universities are also involved.
"This research program by NCAR is a major contribution to the insurance industry and public policymakers," says Rowan Douglas, managing director of Willis. "The primary way to improve our understanding of present and future hurricane risk is to generate computer simulations of storms in unprecedented detail. NCAR's work is at the forefront of this critical line of research, helping those with onshore and offshore risks in the Gulf, and with relevance to all affected by tropical cyclones in the United States and worldwide."
The research plan
For this new NCAR project, researchers will examine three decades in detail: 1995-2005, 2020-2030, and 2045-2055. They will use statistical techniques to fill in the gaps between these decades. A major goal is to examine how several decades of greenhouse-gas buildup could affect regional climate and, in turn, influence hurricanes and other critical weather features. The team will also investigate the impact of the powerful storms on global climate.
 Greg Holland. [ENLARGE] (©UCAR, photo by Carlye Calvin.) News media terms of use*
Greg Holland. [ENLARGE] (©UCAR, photo by Carlye Calvin.) News media terms of use*
One of the most difficult technical challenges for such a project is to create a model that can capture both the climate of the entire world and the behavior of a single hurricane. Models simulate weather conditions at thousands of points in a three-dimensional grid that represents the atmosphere. If the points are spaced far apart, as in a coarse-resolution global climate model, the model will run more quickly on a supercomputer but it cannot simulate a hurricane in realistic detail. Conversely, a high-resolution regional weather model can simulate a hurricane with a core that is just a few miles across, but it may not correctly include factors driven by global-scale warming that could affect hurricane formation, such as changes in wind shear and atmospheric stability.
To get around these roadblocks, NCAR scientists are integrating two of the center's leading models into the Nested Regional Climate Model (NRCM). They nest a special version of their high-resolution weather model (the Weather Research and Forecasting model, or WRF) inside a lower-resolution, global climate model (the Community Climate System Model, or CCSM).
The resulting simulations show fine-scale detail for certain regions, like the Gulf of Mexico, while also incorporating global climate patterns. For each of its decade-long time slices, the NRCM's resolution will be about 20 miles across Africa, Europe, and the South Atlantic; 7.5 miles across the tropical Atlantic and northeastern United States; and an even sharper 2.5 miles over the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico, southeastern United States, and the drought-prone western United States.
"Combining weather and climate models in this way enables more detailed projections of hurricanes in a warming world than any study to date," says Holland. "These projections will help reduce the uncertainty of current assessments, and they also give us experience in predicting changes to other high-impact weather systems."
With its considerable requirements, the project is putting months of intense demand on bluefire, NCAR's flagship supercomputer. Manufactured by IBM, it is ranked as one of the 50 most powerful computers on Earth and can solve up to 76 trillion equations every second.
"The NRCM is one of the most intensive computer simulations we have witnessed at NCAR," says Tom Bettge, director of operations and services for NCAR's Computational and Information Systems Laboratory. "As we evaluate future North American climate in increasing detail, we will look to even bigger and faster high-performance computers."
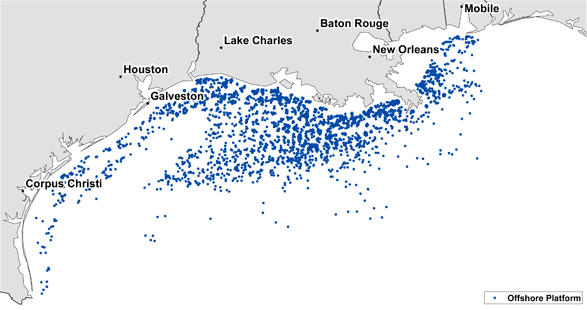
Offshore platforms. The dense cluster of offshore drilling platforms in the Gulf of Mexico is vulnerable to hurricanes. Personnel are often evacuated when a major storm is imminent, and damage to the structures is not uncommon. [ENLARGE] (Image courtesy of the American Petroleum Institute, based on data from the Minerals Management Service of the U.S. Department of the Interior.) News media terms of use*